DP-203: Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
You are implementing an Azure Blob storage account for an application that has the following requirements:
- Data created during the last 12 months must be readily accessible.
- Blobs older than 24 months must use the lowest storage costs. This data will be accessed infrequently.
- Data created 12 to 24 months ago will be accessed infrequently but must be readily accessible at the lowest storage costs.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence?
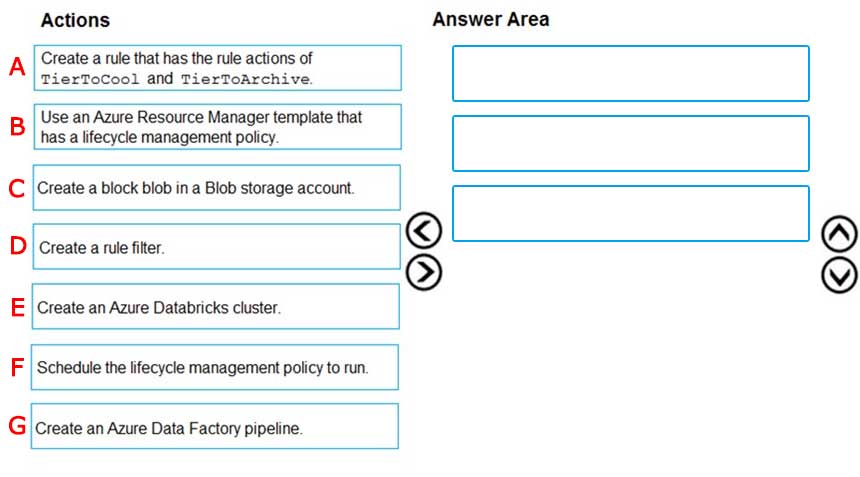
A-F-E
B-A-F
C-B-A
D-C-F
E-A-D
F-A-D
G-C-B
Answer is C-B-A
Step 1: Create a block blob in a Blob storage account
First create the block blob.
Azure Blob storage lifecycle management offers a rich, rule-based policy for GPv2 and Blob storage accounts.
Step 2: Use an Azure Resource Manager template that has a lifecycle management policy
Step 3: Create a rule that has the rule actions of TierToCool and TierToArchive
Each rule definition includes a filter set and an action set. The filter set limits rule actions to a certain set of objects within a container or objects names.
Note: You can add a Rule through Azure portal:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
1. In the Azure portal, search for and select your storage account.
2. Under Blob service, select Lifecycle Management to view or change your rules.
3. Select the List View tab.
4. Select Add a rule and name your rule on the Details form. You can also set the Rule scope, Blob type, and Blob subtype values.
5. Select Base blobs to set the conditions for your rule. For example, blobs are moved to cool storage if they haven't been modified for 30 days.
6. Etc.
Incorrect Answers:
- Schedule the lifecycle management policy to run:
You don't Schedule the lifecycle management policy to run. The platform runs the lifecycle policy once a day. Once you configure a policy, it can take up to 24 hours for some actions to run for the first time.
- Create a rule filter:
No need for a rule filter. Rule filters limit rule actions to a subset of blobs within the storage account.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/blobs/storage-lifecycle-management-concepts
A company uses Microsoft Azure SQL Database to store sensitive company data. You encrypt the data and only allow access to specified users from specified locations.
You must monitor data usage, and data copied from the system to prevent data leakage.
You need to configure Azure SQL Database to email a specific user when data leakage occurs.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence?
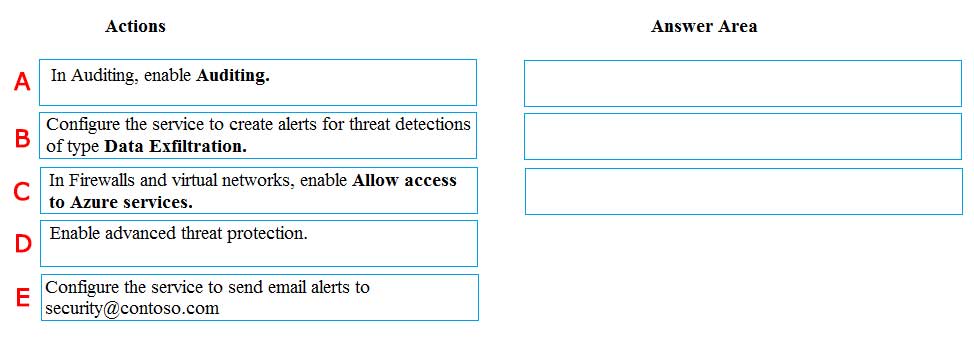
A-B-C
B-A-D
C-D-E
D-E-B
E-B-A
A-D-C
B-C-D
C-B-A
Answer is D-E-B
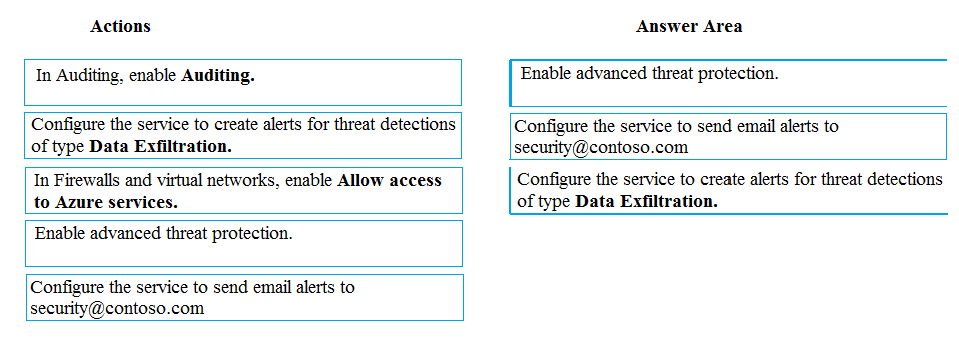
Step 1: Enable advanced threat protection
Set up threat detection for your database in the Azure portal
1. Launch the Azure portal at https://portal.azure.com.
2. Navigate to the configuration page of the Azure SQL Database server you want to protect. In the security settings, select Advanced Data Security.
3. On the Advanced Data Security configuration page:
Enable advanced data security on the server.
In Threat Detection Settings, in the Send alerts to text box, provide the list of emails to receive security alerts upon detection of anomalous database activities.
Step 2: Configure the service to send email alerts to security@contoso.team
Step 3:..of type data exfiltration
The benefits of Advanced Threat Protection for Azure Storage include:
Detection of anomalous access and data exfiltration activities.
Security alerts are triggered when anomalies in activity occur: access from an unusual location, anonymous access, access by an unusual application, data exfiltration, unexpected delete operations, access permission change, and so on.
Admins can view these alerts via Azure Security Center and can also choose to be notified of each of them via email.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-threat-detection
https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2019/04/04/microsoft-azure-security/
You have an Azure Synapse Analytics SQL pool named Pool1 on a logical Microsoft SQL server named Server1.
You need to implement Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) on Pool1 by using a custom key named key1.
Which five actions should you perform in sequence?
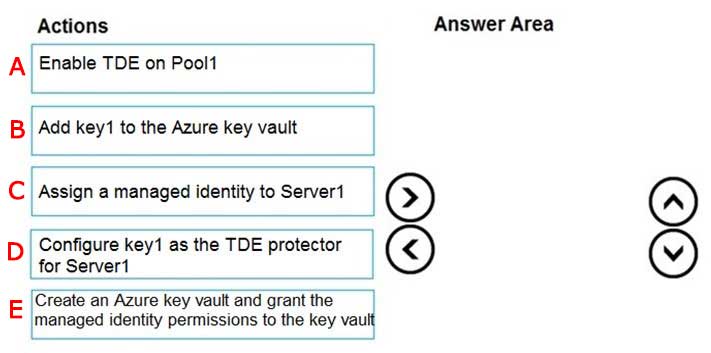
Check the answer section
Answer is

Step 1: Assign a managed identity to Server1
You will need an existing Managed Instance as a prerequisite.
Step 2: Create an Azure key vault and grant the managed identity permissions to the vault
Create Resource and setup Azure Key Vault.
Step 3 :Add key1 to the Azure key vault
The recommended way is to import an existing key from a .pfx file or get an existing key from the vault. Alternatively, generate a new key directly in Azure Key Vault.
Step 4: Configure key1 as the TDE protector for Server1
Provide TDE Protector key
Step 5: Enable TDE on Pool1
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/managed-instance/scripts/transparent-data-encryption-byok-powershell
You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant that contains a security group named Group1. You have an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool named dw1 that contains a schema named schema1.
You need to grant Group1 read-only permissions to all the tables and views in schema1. The solution must use the principle of least privilege.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence?

Check the answer section
D: Create a database user in dw1 that represents Group1 and uses FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDE clause
A: Create a database role named Role1 and grant Role1 SELECT permissions to schema1
E: Assign Rol1 to the Group1 database user
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/data-share/how-to-share-from-sql
You have an ASP.NET web app that uses an Azure SQL database. The database contains a table named Employee. The table contains sensitive employee information, including a column named DateOfBirth.
You need to ensure that the data in the DateOfBirth column is encrypted both in the database and when transmitted between a client and Azure. Only authorized clients must be able to view the data in the column.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence?
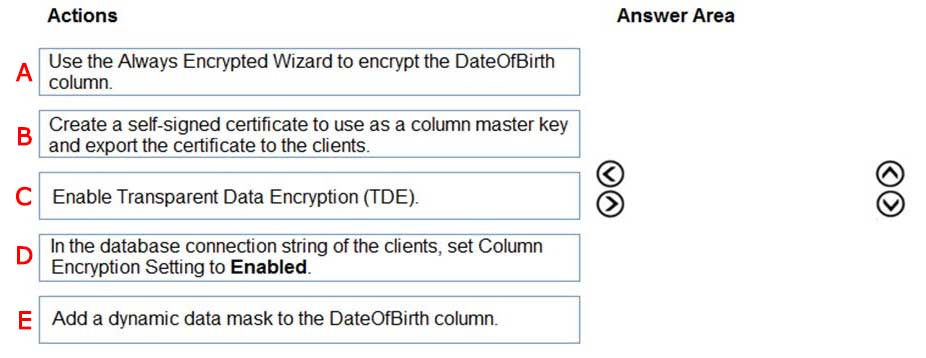
Check the answer section
Answer is
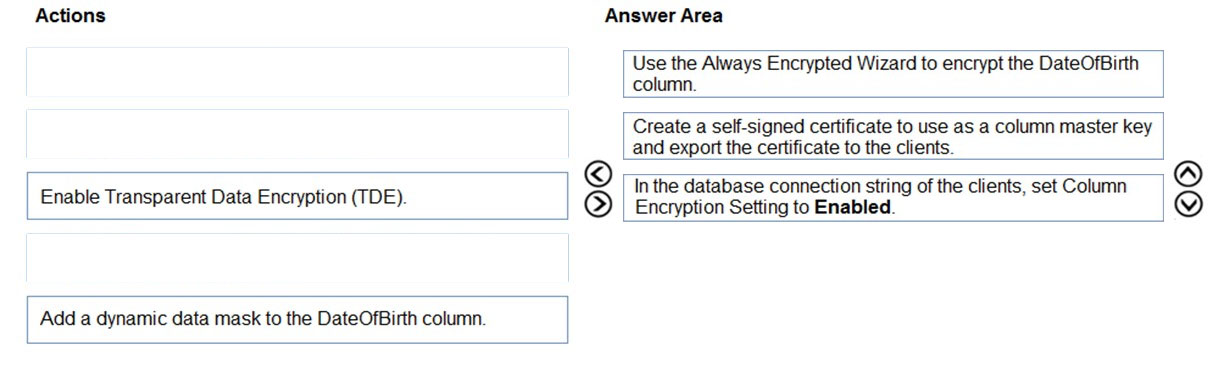
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-always-encrypted
You have an Azure data factory. You need to ensure that pipeline-run data is retained for 120 days. The solution must ensure that you can query the data by using the Kusto query language.
Which four actions should you perform in sequence?
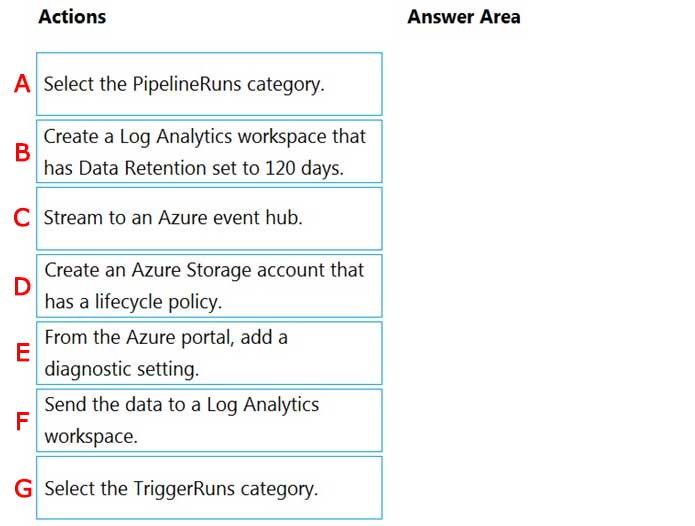
Check the answer section
Storage account is not needed here.
Step 1: Create a Log Analytics workspace that has Data Retention set to 120 days.
Step 2: From Azure Portal, add a diagnostic setting.
Step 3: Select the PipelineRuns Category
Step 4: Send the data to a Log Analytics workspace.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/data-factory/monitor-using-azure-monitor
You deploy an Azure SQL database named DB1 to an Azure SQL server named SQL1.
Currently, only the server admin has access to DB1.
An Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) group named Analysts contains all the users who must have access to DB1.
You have the following data security requirements:
- The Analysts group must have read-only access to all the views and tables in the Sales schema of DB1.
- A manager will decide who can access DB1. The manager will not interact directly with DB1.
- Users must not have to manage a separate password solely to access DB1.
Which four actions should you perform in sequence to meet the data security requirements?
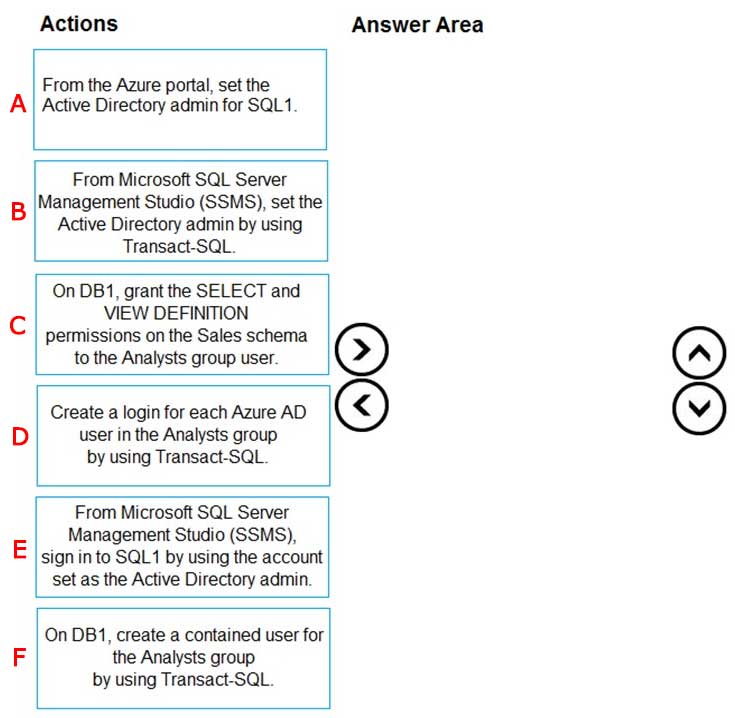
Check the answer section
Answer is
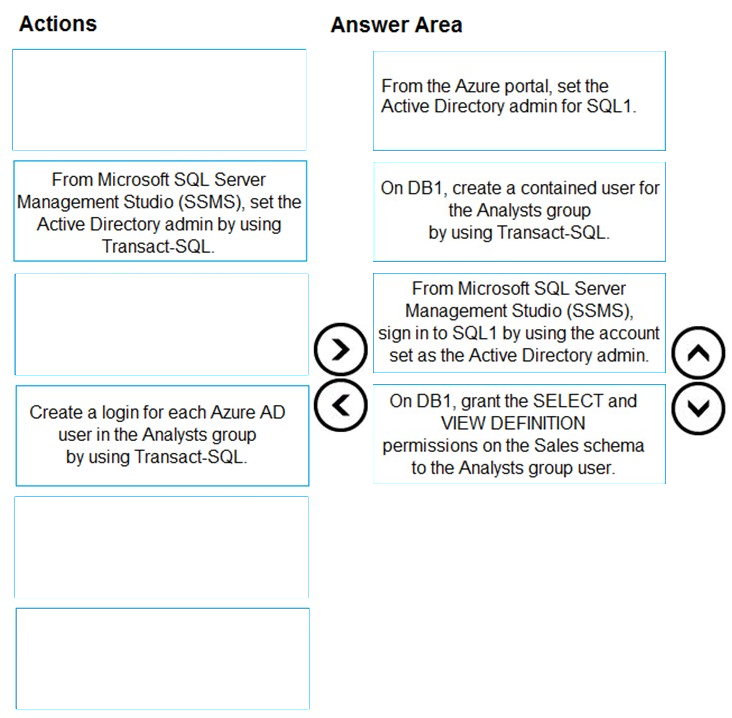
Step 1: From the Azure Portal, set the Active Directory admin for SQL1.
Provision an Azure Active Directory administrator for your Azure SQL Database server.
You can provision an Azure Active Directory administrator for your Azure SQL server in the Azure portal and by using PowerShell.
Step 2: On DB1, create a contained user for the Analysts group by using Transact-SQL
Create contained database users in your database mapped to Azure AD identities.
To create an Azure AD-based contained database user (other than the server administrator that owns the database), connect to the database with an Azure AD identity, as a user with at least the ALTER ANY USER permission. Then use the following Transact-SQL syntax:
CREATE USER
Step 3: From Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), sign in to SQL1 by using the account set as the Active Directory admin.
Connect to the user database or data warehouse by using SSMS or SSDT
To confirm the Azure AD administrator is properly set up, connect to the master database using the Azure AD administrator account. To provision an Azure AD- based contained database user (other than the server administrator that owns the database), connect to the database with an Azure AD identity that has access to the database.
Step 4: On DB1, grant the VIEW and SELECT DEFINTION.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-aad-authentication-configure
You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Databricks environment and an Azure Storage account.
You need to implement secure communication between Databricks and the storage account.
You create an Azure key vault.
Which four actions should you perform in sequence?
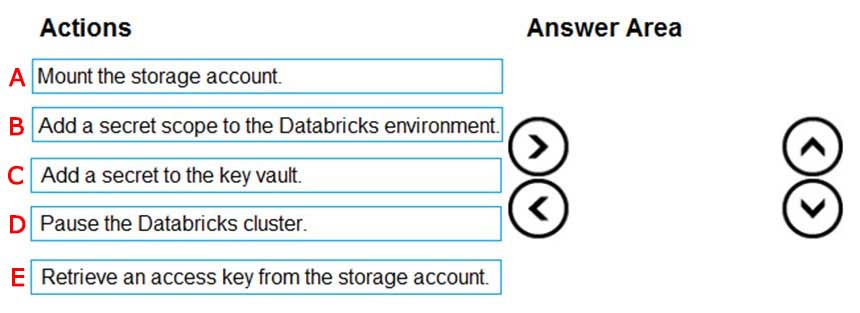
Check the answer section
Answer is

Step 1: Mount the storage account
Step 2: Retrieve an access key from the storage account.
Step 3: Add a secret to the key vault.
Step 4: Add a secret scope to the Databricks environment.
Managing secrets begins with creating a secret scope.
To reference secrets stored in an Azure Key Vault, you can create a secret scope backed by Azure Key Vault.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-databricks/store-secrets-azure-key-vault
You have data stored in thousands of CSV files in Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2. Each file has a header row followed by a property formatted carriage return (/r) and line feed (/n).
You are implementing a pattern that batch loads the files daily into an enterprise data warehouse in Azure Synapse Analytics by using PolyBase. You need to skip the header row when you import the files into the data warehouse. Before building the loading pattern, you need to prepare the required database objects in Azure Synapse Analytics.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence?
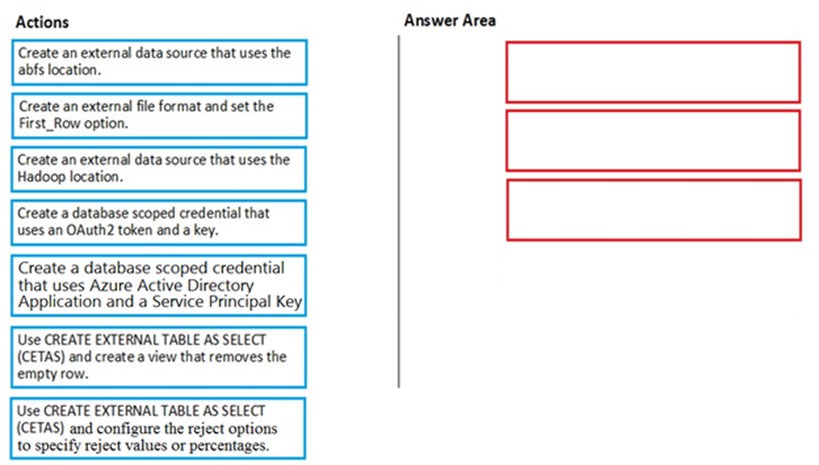
Check the answer section
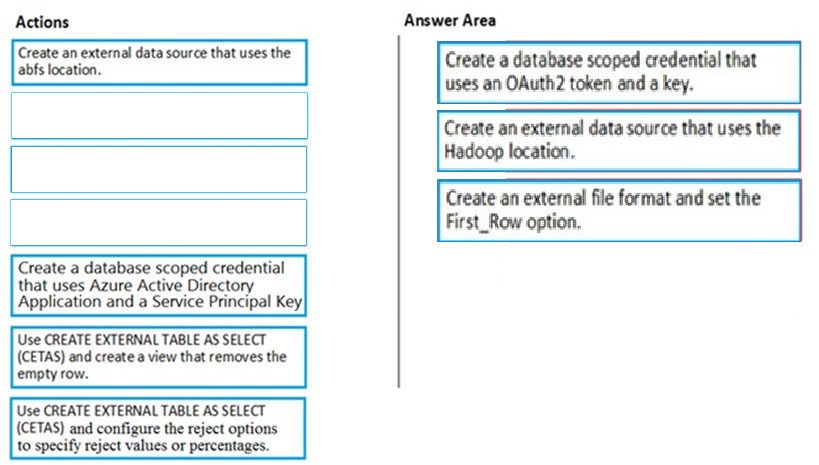
Step 1: Create a database scoped credential that uses OAuth2 token and a key.
CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL creates a database credential. A database credential is not mapped to a server login or database user. The credential is used by the database to access to the external location anytime the database is performing an operation that requires access. The following example creates a database scoped credential that can be used to create an external data source, which can be used by PolyBase in Azure Synapse Analytics.
Azure Data Lake Store uses an Azure Active Directory Application for Service to Service Authentication. Please create an AAD application and document your client_id, OAuth_2.0_Token_EndPoint, and Key before you try to create a database scoped credential.
-- Create a db master key if one does not already exist, using your own password.
CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD=
-- Create a database scoped credential.
CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL ADL_User
WITH
IDENTITY = '
SECRET = '
Step 2: Create an external data source that uses the Hadoop location.
Use HADOOP when the external data source is Cloudera, Hortonworks, or an Azure Storage account.
Incorrect:
abfs or abfss APIs are not supported when accessing Azure Storage Accounts.
Step 3: Create an external file format and set the First_Row option.
Creates an External File Format object defining external data stored in Hadoop, Azure Blob Storage, or Azure Data Lake Store. Creating an external file format is a prerequisite for creating an External Table.
FIRST_ROW = First_row_int
Specifies the row number that is read first in all files during a PolyBase load. This parameter can take values 1-15. If the value is set to two, the first row in every file (header row) is skipped when the data is loaded. Rows are skipped based on the existence of row terminators (/r/n, /r, /n).
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/statements/create-database-scoped-credential-transact-sql
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/statements/create-external-data-source-transact-sql
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/statements/create-external-file-format-transact-sql
You have a table named SalesFact in an enterprise data warehouse in Azure Synapse Analytics. SalesFact contains sales data from the past 36 months and has the following characteristics:
- Is partitioned by month
- Contains one billion rows
- Has clustered columnstore indexes
At the beginning of each month, you need to remove data from SalesFact that is older than 36 months as quickly as possible.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence in a stored procedure?

Check the answer section
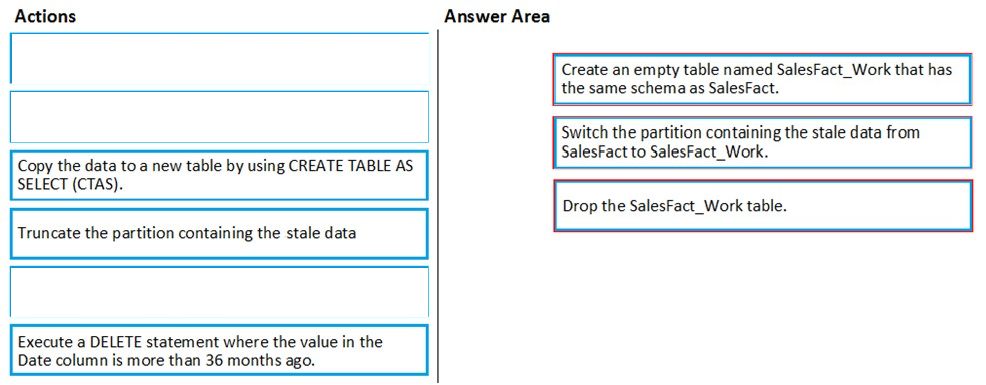
Step 1: Create an empty table named SalesFact_work that has the same schema as SalesFact.
Step 2: Switch the partition containing the stale data from SalesFact to SalesFact_Work.
SQL Data Warehouse supports partition splitting, merging, and switching. To switch partitions between two tables, you must ensure that the partitions align on their respective boundaries and that the table definitions match.
Loading data into partitions with partition switching is a convenient way stage new data in a table that is not visible to users the switch in the new data.
Step 3: Drop the SalesFact_Work table.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-data-warehouse/sql-data-warehouse-tables-partition