DP-203: Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
You are developing the data platform for a global retail company. The company operates during normal working hours in each region. The analytical database is used once a week for building sales projections.
Each region maintains its own private virtual network.
Building the sales projections is very resource intensive and generates upwards of 20 terabytes (TB) of data.
Microsoft Azure SQL Databases must be provisioned.
• Database provisioning must maximize performance and minimize cost
• The daily sales for each region must be stored in an Azure SQL Database instance
• Once a day, the data for all regions must be loaded in an analytical Azure SQL Database instance
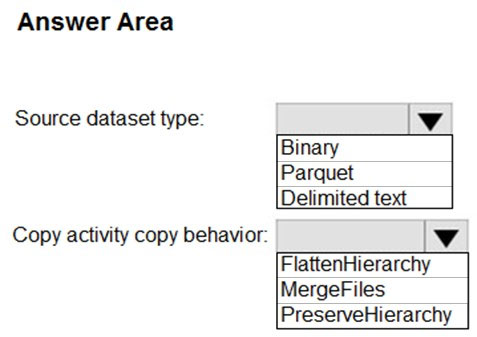
You need to provision Azure SQL database instances.
How should you provision the database instances?
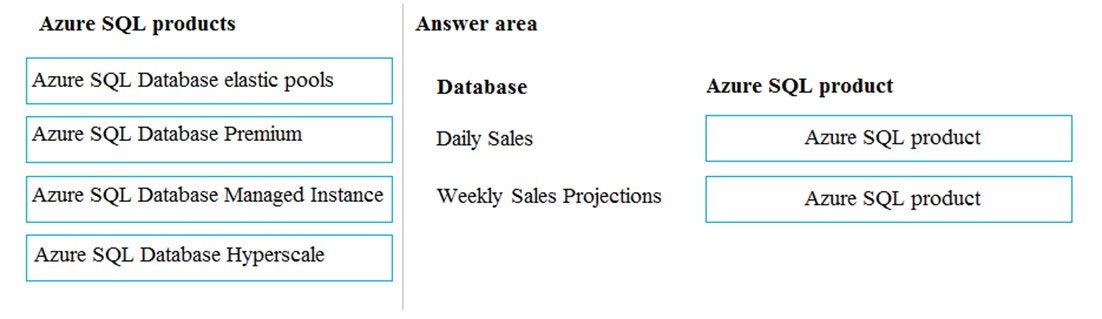
Box 1: Azure SQL Database elastic pools
SQL Database elastic pools are a simple, cost-effective solution for managing and scaling multiple databases that have varying and unpredictable usage demands. The databases in an elastic pool are on a single Azure SQL Database server and share a set number of resources at a set price. Elastic pools in Azure SQL Database enable SaaS developers to optimize the price performance for a group of databases within a prescribed budget while delivering performance elasticity for each database.
BBox 2: Azure SQL Database Hyperscalels
A Hyperscale database is an Azure SQL database in the Hyperscale service tier that is backed by the Hyperscale scale-out storage technology. A Hyperscale database supports up to 100 TB of data and provides high throughput and performance, as well as rapid scaling to adapt to the workload requirements. Scaling is transparent to the application connectivity, query processing, and so on, work like any other SQL database.
BIncorrect Answers:ls
Azure SQL Database Managed Instance: The managed instance deployment model is designed for customers looking to migrate a large number of apps from on- premises or IaaS, self-built, or ISV provided environment to fully managed PaaS cloud environment, with as low migration effort as possible.
BReferences:ls
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-elastic-pool
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-service-tier-hyperscale-faq
A company is deploying a service-based data environment. You are developing a solution to process this data.
The solution must meet the following requirements:
- Use an Azure HDInsight cluster for data ingestion from a relational database in a different cloud service
- Use an Azure Data Lake Storage account to store processed data
- Allow users to download processed data
You need to recommend technologies for the solution.
Which technologies should you use?
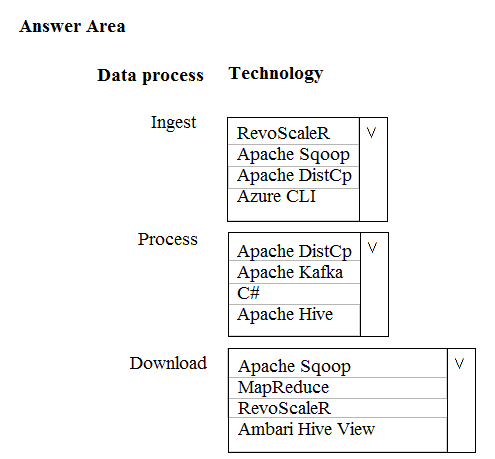
Box 1: Apache Sqoop
Apache Sqoop is a tool designed for efficiently transferring bulk data between Apache Hadoop and structured datastores such as relational databases.
Azure HDInsight is a cloud distribution of the Hadoop components from the Hortonworks Data Platform (HDP).
Incorrect Answers:
DistCp (distributed copy) is a tool used for large inter/intra-cluster copying. It uses MapReduce to effect its distribution, error handling and recovery, and reporting.
It expands a list of files and directories into input to map tasks, each of which will copy a partition of the files specified in the source list. Its MapReduce pedigree has endowed it with some quirks in both its semantics and execution.
RevoScaleR is a collection of proprietary functions in Machine Learning Server used for practicing data science at scale. For data scientists, RevoScaleR gives you data-related functions for import, transformation and manipulation, summarization, visualization, and analysis.
Box 2: Apache Hive
Box 3: Ambari Hive View
You can run Hive queries by using Apache Ambari Hive View. The Hive View allows you to author, optimize, and run Hive queries from your web browser.
References:
https://sqoop.apache.org/
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/hdinsight/hadoop/apache-hadoop-use-hive-ambari-view
You develop data engineering solutions for a company.
A project requires an in-memory batch data processing solution.
You need to provision an HDInsight cluster for batch processing of data on Microsoft Azure.
How should you complete the PowerShell segment?

Box 1: New-AzStorageContainer
# Example: Create a blob container. This holds the default data store for the cluster.
New-AzStorageContainer
-Name $clusterName
-Context $defaultStorageContext
$sparkConfig = New-Object "System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary``2[System.String,System.String]"
$sparkConfig.Add("spark", "2.3")
Box 2: Spark
Spark provides primitives for in-memory cluster computing. A Spark job can load and cache data into memory and query it repeatedly. In-memory computing is much faster than disk-based applications than disk-based applications, such as Hadoop, which shares data through Hadoop distributed file system (HDFS).
Box 3: New-AzureRMHDInsightCluster
# Create the HDInsight cluster. Example:
New-AzHDInsightCluster `
-ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName `
-ClusterName $clusterName `
-Location $location `
-ClusterSizeInNodes $clusterSizeInNodes `
-ClusterType $"Spark" `
-OSType "Linux" `
Box 4: Spark
HDInsight is a managed Hadoop service. Use it deploy and manage Hadoop clusters in Azure. For batch processing, you can use Spark, Hive, Hive LLAP, MapReduce.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/bs-latn-ba/azure/hdinsight/spark/apache-spark-jupyter-spark-sql-use-powershell
https://docs.microsoft.com/bs-latn-ba/azure/hdinsight/spark/apache-spark-overview
You have an Azure Storage account named storage1 that is configured as shown in the following exhibit.
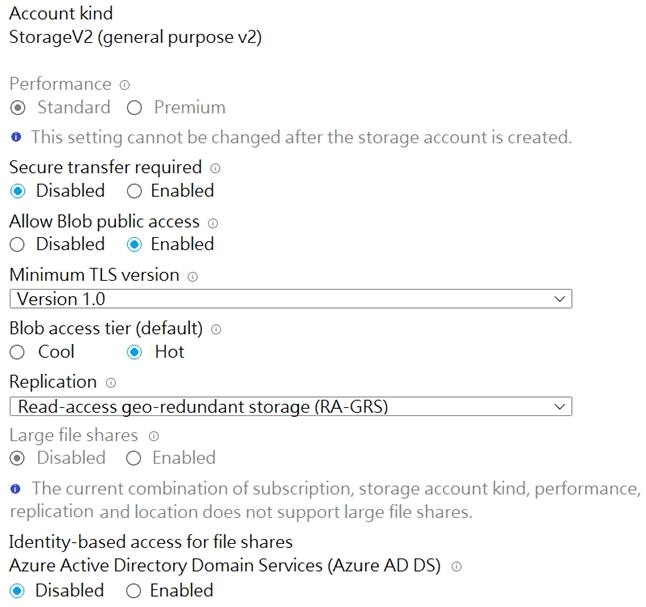
You need to ensure that all calls to an Azure Storage REST API operation on storage1 are made over HTTPS.
What should you do?
Set Secure transfer required to Enabled.
Set Allow Blob public access to Disabled.
For the Blob service, create a shared access signature (SAS) that allows HTTPS only.
Set Minimum TLS version to Version 1.2.
Answer is Set Secure transfer required to Enabled.
You can configure your storage account to accept requests from secure connections only by setting the Secure transfer required property for the storage account.
When you require secure transfer, any requests originating from an insecure connection are rejected. Microsoft recommends that you always require secure transfer for all of your storage accounts.
When secure transfer is required, a call to an Azure Storage REST API operation must be made over HTTPS. Any request made over HTTP is rejected.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/common/storage-require-secure-transfer
A company runs Microsoft Dynamics CRM with Microsoft SQL Server on-premises. SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) packages extract data from Dynamics CRM APIs, and load the data into a SQL Server data warehouse.
The datacenter is running out of capacity. Because of the network configuration, you must extract on premises data to the cloud over https. You cannot open any additional ports. The solution must implement the least amount of effort.
You need to create the pipeline system.
Which component should you use?
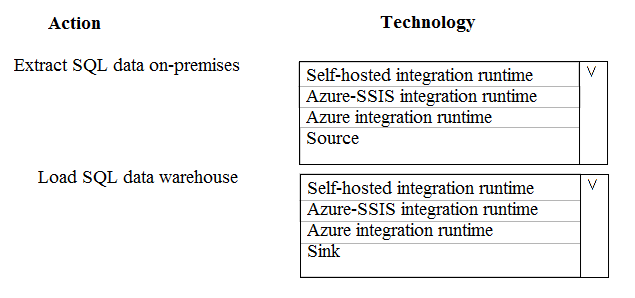
Box 1: Box 2: Self-hosted integration runtime
Box 2: Self-hosted integration runtime
A self-hosted integration runtime can run copy activities between a cloud data store and a data store in a private network, and it can dispatch transform activities against compute resources in an on-premises network or an Azure virtual network. The installation of a self-hosted integration runtime needs on an on-premises machine or a virtual machine (VM) inside a private network.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/data-factory/create-self-hosted-integration-runtime
You are designing an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 structure for telemetry data from 25 million devices distributed across seven key geographical regions. Each minute, the devices will send a JSON payload of metrics to Azure Event Hubs.
You need to recommend a folder structure for the data. The solution must meet the following requirements:
- Data engineers from each region must be able to build their own pipelines for the data of their respective region only.
- The data must be processed at least once every 15 minutes for inclusion in Azure Synapse Analytics serverless SQL pools.
How should you recommend completing the structure? To answer, drag the appropriate values to the correct targets. Each value may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.

Answer is {raw/regionID}/{YYYY}/{MM}/{DD}/{HH}/{mm}/{deviceID}.json
{raw/regionID} is the first level because raw is the container name for the raw data. RegionID follows it for ease of managing security.
{YYYY}/{MM}/{DD}/{HH}/{mm}/{deviceID}.json instead of {deviceID}/{YYYY}/{MM}/{DD}/{HH}/{mm}.json. The primary reason is that you want your namespace structure to have as few folders as high up and narrow those down as you get deeper into your structure.
For example, if you have 1 year worth of data and 25 million devices, using {YYYY}/{MM}/{DD}/{HH}/{mm}/ results in 2.1 million folders (1 year * 12 months * 30 days [estimate] * 24 hours * 60 minutes). If you start your folder structure with {deviceID}, you end up with 25 million folders - one for each device - before you even get to including the date in the hierarchy.
Reference:
https://github.com/paolosalvatori/StreamAnalyticsAzureDataLakeStore/blob/master/README.md
You have an enterprise-wide Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account. The data lake is accessible only through an Azure virtual network named VNET1.
You are building a SQL pool in Azure Synapse that will use data from the data lake.
Your company has a sales team. All the members of the sales team are in an Azure Active Directory group named Sales. POSIX controls are used to assign the
Sales group access to the files in the data lake.
You plan to load data to the SQL pool every hour.
You need to ensure that the SQL pool can load the sales data from the data lake.
Which three actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
Add the managed identity to the Sales group.
Use the managed identity as the credentials for the data load process.
Create a shared access signature (SAS).
Add your Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) account to the Sales group.
Use the shared access signature (SAS) as the credentials for the data load process.
Create a managed identity.