DP-203: Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
What is an Azure SQL logical server?
An administrative container for your databases.
Another name for an Azure SQL database instance.
A server that defines the logical rules that sort and compare data
Answer is An administrative container for your databases.
Azure SQL logical server is an administrative container for your databases. You can control logins, firewall rules, and security policies through the logical server. It is not another name for an Azure SQL Database instance and Collations are rules that sort and compare data.
Your Azure SQL database provides adequate storage and compute power. But you find that you need additional IO throughput. Which performance model might you use?
DTU
vCore
SQL elastic pool
Answer is vCore
vCore gives you greater control over what compute and storage resources you create and pay for. You can increase IO throughput but keep the existing amount of compute and storage.
DTU, or Database Transaction Unit, provides a simple, preconfigured purchase option. To increase IO throughput, you would need to move to a higher tier that also increases your storage and compute power, things you don't need.
SQL elastic pools enable you to buy a set of compute and storage resources that are shared among all the databases in the pool. This option won't help with IO performance because you're working with just one database.
The following query is to retrieve the sales by business reseller, but the performance of the query is slow. The query is as follows:
SELECT S.[SalesAmount] AS [Sales], R.[BusinessType], R.[ResellerName] FROM [FactResellerSales] AS S JOIN [DimReseller] AS R ON S.[ResellerKey] = R.[ResellerKey].The tables referenced within the query are configured with a distribution of Round_Robin with a clustered columnstore index. The Data Engineer wants to improve the performance of the query. What operation can be used to improve the performance of the query?
Remove the CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX for both tables.
Change the Distribution to HASH(GeographyKey) for both tables.
Change the Distribution to HASH(ResellerKey) for both tables.
Answer is Change the Distribution to HASH(ResellerKey) for both tables.
Placing Hash distribution on the ResellerKey on both the FactResellerSales and DimReseller will improve the performance of the query. Placing Hash distribution on the GeographyKey on both the FactResellerSales and DimReseller will not help the the performance of this query. Removing the CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX for both tables would reduce the performance of this query.
Mike is the data engineer for Contoso and has a Data Warehouse created with a database name Crystal. He has created a master key, followed by a database scoped credential. What should he create next?
An external data source.
An external table.
A physical table.
Answer is An external data source.
An external data source. Once the master key and the database scoped credential is created, Mike should create an external data source that contains a url to the Blob location and the name of the database scoped credential. Mike must have an external data source before he creates an external table and he must have an external data source and an external table before he can create a physical table.
You have an Azure SQL data warehouse.
Using PolyBase, you CREATE table named [Ext].[Items] to query Parquet files stored in Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 without importing the data to the data warehouse.
The external table has three columns.
You discover that the Parquet files have a fourth column named ItemID.
Which command should you run to add the ItemID column to the external table?
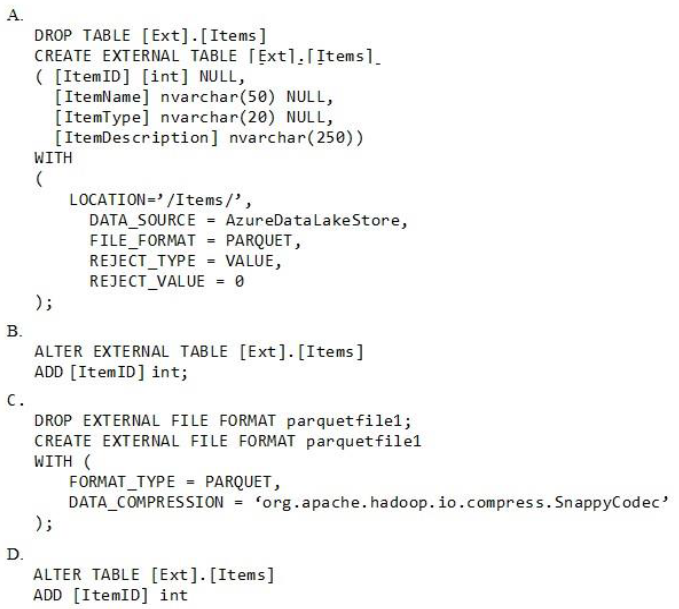
Option A
Option B
Option C
Option D
Answer is Option A
Only these Data Definition Language (DDL) statements are allowed on external tables:
- CREATE TABLE and DROP TABLE
- CREATE STATISTICS and DROP STATISTICS
- CREATE VIEW and DROP VIEW
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/statements/create-external-table-transact-sql
You develop a data ingestion process that will import data to a Microsoft Azure SQL Data Warehouse. The data to be ingested resides in parquet files stored in an Azure Data Lake Gen 2 storage account.
You need to load the data from the Azure Data Lake Gen 2 storage account into the Azure SQL Data Warehouse.
Solution:
- 1. Use Azure Data Factory to convert the parquet files to CSV files
- 2. Create an external data source pointing to the Azure storage account
- 3. Create an external file format and external table using the external data source
- 4. Load the data using the INSERT…SELECT statement
Yes
No
Answer is No
There is no need to convert the parquet files to CSV files.
You load the data using the CREATE TABLE AS SELECT statement.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-data-warehouse/sql-data-warehouse-load-from-azure-data-lake-store
You develop a data ingestion process that will import data to a Microsoft Azure SQL Data Warehouse. The data to be ingested resides in parquet files stored in an Azure Data Lake Gen 2 storage account.
You need to load the data from the Azure Data Lake Gen 2 storage account into the Azure SQL Data Warehouse.
Solution:
- 1. Create an external data source pointing to the Azure storage account
- 2. Create a workload group using the Azure storage account name as the pool name
- 3. Load the data using the INSERT…SELECT statement
Yes
No
Answer is No
You need to create an external file format and external table using the external data source.
You then load the data using the CREATE TABLE AS SELECT statement.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-data-warehouse/sql-data-warehouse-load-from-azure-data-lake-store
A company uses Azure SQL Database to store sales transaction data. Field sales employees need an offline copy of the database that includes last year’s sales on their laptops when there is no internet connection available.
You need to create the offline export copy.
Which three options can you use?
Export to a BACPAC file by using Azure Cloud Shell, and save the file to an Azure storage account
Export to a BACPAC file by using SQL Server Management Studio. Save the file to an Azure storage account
Export to a BACPAC file by using the Azure portal
Export to a BACPAC file by using Azure PowerShell and save the file locally
Export to a BACPAC file by using the SqlPackage utility
Answers are; Export to a BACPAC file by using SQL Server Management Studio. Save the file to an Azure storage account
Export to a BACPAC file by using the Azure portal
Export to a BACPAC file by using the SqlPackage utility
You can export to a BACPAC file using the Azure portal.
You can export to a BACPAC file using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). The newest versions of SQL Server Management Studio provide a wizard to export an Azure SQL database to a BACPAC file.
You can export to a BACPAC file using the SQLPackage utility.
Incorrect Answers:
D: You can export to a BACPAC file using PowerShell. Use the New-AzSqlDatabaseExport cmdlet to submit an export database request to the Azure SQL Database service. Depending on the size of your database, the export operation may take some time to complete. However, the file is not stored locally.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-export
You develop a data ingestion process that will import data to a Microsoft Azure SQL Data Warehouse. The data to be ingested resides in parquet files stored in an Azure Data Lake Gen 2 storage account.
You need to load the data from the Azure Data Lake Gen 2 storage account into the Azure SQL Data Warehouse.
Solution:
1. Create an external data source pointing to the Azure Data Lake Gen 2 storage account
2. Create an external file format and external table using the external data source
3. Load the data using the CREATE TABLE AS SELECT statement
Does the solution meet the goal?
Yes
No
Answer is Yes
You need to create an external file format and external table using the external data source.
You load the data using the CREATE TABLE AS SELECT statement.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-data-warehouse/sql-data-warehouse-load-from-azure-data-lake-store
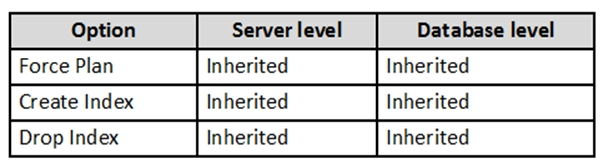
You are implementing automatic tuning mode for Azure SQL databases.
Automatic tuning is configured as shown in the following table.
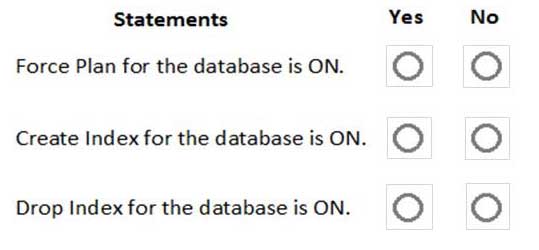
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
No - No - No
No - No - Yes
No - Yes - No
No - Yes - Yes
Yes - No - No
Yes - No - Yes
Yes - Yes - No
Yes - Yes - Yes
Answer is Yes - Yes - No
Automatic tuning options can be independently enabled or disabled per database, or they can be configured on SQL Database servers and applied on every database that inherits settings from the server. SQL Database servers can inherit Azure defaults for Automatic tuning settings. Azure defaults at this time are set to FORCE_LAST_GOOD_PLAN is enabled, CREATE_INDEX is enabled, and DROP_INDEX is disabled.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-automatic-tuning