DP-203: Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
Your company uses Azure SQL Database and Azure Blob storage.
All data at rest must be encrypted by using the company’s own key. The solution must minimize administrative effort and the impact to applications which use the database.
You need to configure security.
What should you implement?
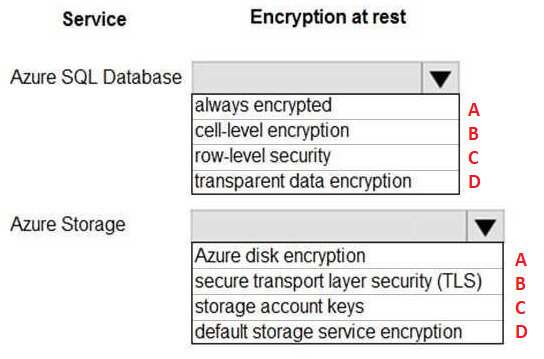
A-B
B-C
C-D
D-C
B-D
C-A
D-B
A-C
Answer is
Box 1: transparent data encryption
TDE with customer-managed keys in Azure Key Vault allows to encrypt the Database Encryption Key (DEK) with a customer-managed asymmetric key called TDE Protector. This is also generally referred to as Bring Your Own Key (BYOK) support for Transparent Data Encryption.
Note: Transparent data encryption encrypts the storage of an entire database by using a symmetric key called the database encryption key. This database encryption key is protected by the transparent data encryption protector.
Transparent data encryption (TDE) helps protect Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Managed Instance, and Azure Data Warehouse against the threat of malicious offline activity by encrypting data at rest. It performs real-time encryption and decryption of the database, associated backups, and transaction log files at rest without requiring changes to the application.
Box 2: Storage account keys
You can rely on Microsoft-managed keys for the encryption of your storage account, or you can manage encryption with your own keys, together with Azure Key Vault.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/transparent-data-encryption-azure-sql
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/common/storage-service-encryption
You have an Azure subscription that contains the following resources:
- An Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant that contains a security group named Group1
- An Azure Synapse Analytics SQL pool named Pool1
You need to control the access of Group1 to specific columns and rows in a table in Pool1.
Which Transact-SQL commands should you use?
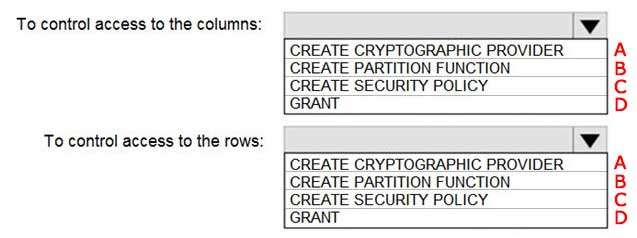
A-B
B-C
C-D
D-C
A-D
B-A
C-C
D-B
Answer is D - C
Box 1: GRANT
You can implement column-level security with the GRANT T-SQL statement.
Box 2: CREATE SECURITY POLICY
Implement Row Level Security by using the CREATE SECURITY POLICY Transact-SQL statement
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql-data-warehouse/column-level-security
You have a data warehouse in Azure Synapse Analytics.
You need to ensure that the data in the data warehouse is encrypted at rest.
What should you enable?
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE)
Secure transfer required
Always Encrypted for all columns
Advanced Data Security for this database
Answer is Transparent Data Encryption (TDE)
Azure SQL Database currently supports encryption at rest for Microsoft-managed service side and client-side encryption scenarios.
- Support for server encryption is currently provided through the SQL feature called Transparent Data Encryption.
- Client-side encryption of Azure SQL Database data is supported through the Always Encrypted feature.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/security/fundamentals/encryption-atrest
You have an Azure SQL database that contains a table named Customer. Customer contains the columns shown in the following table.
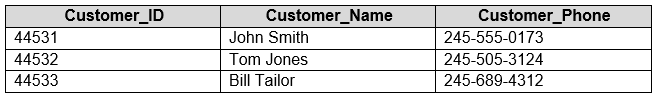
You plan to implement a dynamic data mask for the Customer_Phone column. The mask must meet the following requirements:
- The first six numerals of the customer phone numbers must be masked.
- The last four digits of the customer phone numbers must be visible.
- Hyphens must be preserved and displayed.
How should you configure the dynamic data mask?
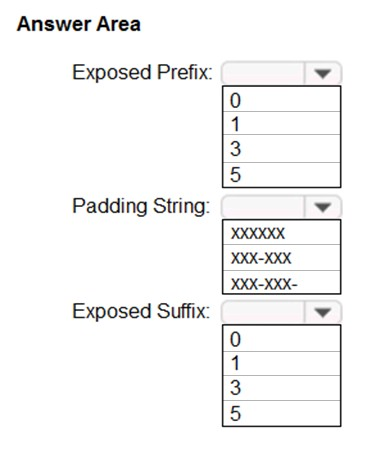
Check the answer section
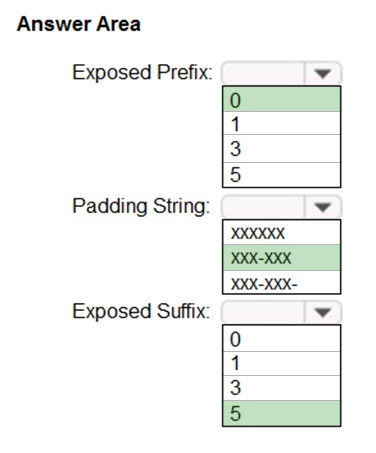
Exposed Prefix: 0
The first six digits must be masked. There is thus no exposed prefix.
Padding String: XXX-XXX
The first six digits must be masked and hyphens must be preserved.
Exposed Suffix: 5
The last 4 digits must be visible. There is not option for 4 but we can use 5 as it would include the hyphen before the last 4 digits.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/security/dynamic-data-masking?view=sql-server-ver15
You manage a financial computation data analysis process. Microsoft Azure virtual machines (VMs) run the process in daily jobs, and store the results in virtual hard drives (VHDs.)
The VMs product results using data from the previous day and store the results in a snapshot of the VHD. When a new month begins, a process creates a new VHD.
You must implement the following data retention requirements:
- Daily results must be kept for 90 days
- Data for the current year must be available for weekly reports
- Data from the previous 10 years must be stored for auditing purposes
- Data required for an audit must be produced within 10 days of a request
How should you configure the lifecycle policy?
Each JSON segment may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bat between panes or scroll to view content.


You are developing a solution to visualize multiple terabytes of geospatial data.
The solution has the following requirements:
- Data must be encrypted.
- Data must be accessible by multiple resources on Microsoft Azure.
Which four actions should you perform in sequence?
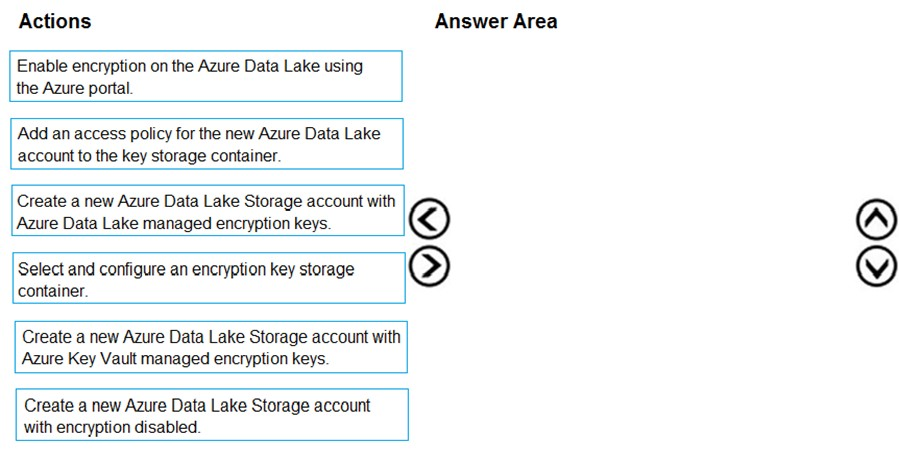
1. Create a new Azure Data Lake Storage account with Azure Key Vault managed encryption keys.
2. Select and configure an encrytion key storage container.
3. Add an access policy for the new Azure Data Lake account to the key storage container
4. Enable encryption on the Azure Data Lake using the Azure Portal
Create a new Azure Data Lake Storage account with Azure Data Lake managed encryption keys
For Azure services, Azure Key Vault is the recommended key storage solution and provides a common management experience across services. Keys are stored and managed in key vaults, and access to a key vault can be given to users or services. Azure Key Vault supports customer creation of keys or import of customer keys for use in customer-managed encryption key scenarios.
Note: Data Lake Storage Gen1 account Encryption Settings. There are three options:
- Do not enable encryption.
- Use keys managed by Data Lake Storage Gen1, if you want Data Lake Storage Gen1 to manage your encryption keys.
- Use keys from your own Key Vault. You can select an existing Azure Key Vault or create a new Key Vault. To use the keys from a Key Vault, you must assign permissions for the Data Lake Storage Gen1 account to access the Azure Key Vault.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/security/fundamentals/encryption-atrest
You are responsible for providing access to an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account.
Your user account has contributor access to the storage account, and you have the application ID access key.
You plan to use PolyBase to load data into Azure SQL data warehouse.
You need to configure PolyBase to connect the data warehouse to the storage account.
Which three components should you create in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate components from the list of components to the answer are and arrange them in the correct order.
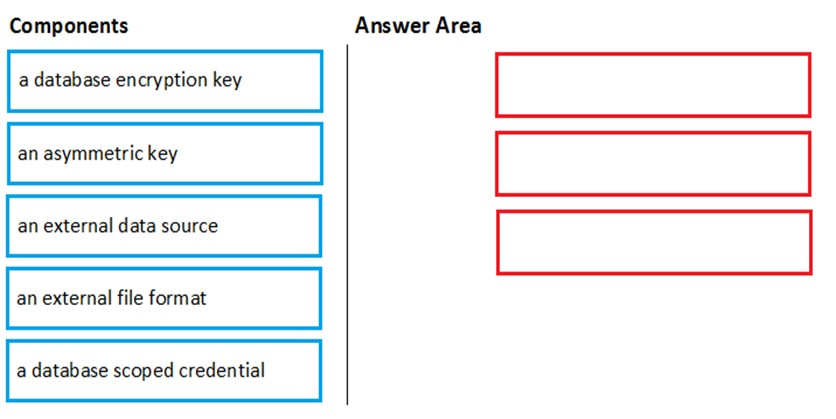
Step 1: a database scoped credential
To access your Data Lake Storage account, you will need to create a Database Master Key to encrypt your credential secret used in the next step. You then create a database scoped credential.
Step 2: an external data source
Create the external data source. Use the CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE command to store the location of the data. Provide the credential created in the previous step.
Step 3: an external file format
Configure data format: To import the data from Data Lake Storage, you need to specify the External File Format. This object defines how the files are written in Data Lake Storage.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-data-warehouse/sql-data-warehouse-load-from-azure-data-lake-store
You have an Azure SQL database that contains a table named Employee. Employee contains sensitive data in a decimal (10,2) column named Salary.
You need to ensure that nonprivileged users can view the table data, but Salary must display a number from 0 to 100.
What should you configure?
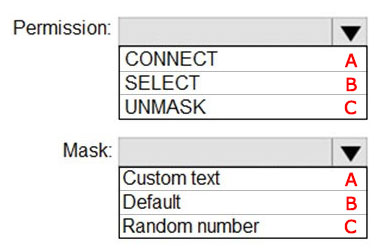
Answer is B-C
Box 1: SELECT
Users with SELECT permission on a table can view the table data. Columns that are defined as masked, will display the masked data.
Incorrect:
Grant the UNMASK permission to a user to enable them to retrieve unmasked data from the columns for which masking is defined.
The CONTROL permission on the database includes both the ALTER ANY MASK and UNMASK permission.
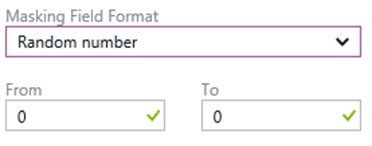
Box 2: Random number
Random number: Masking method, which generates a random number according to the selected boundaries and actual data types. If the designated boundaries are equal, then the masking function is a constant number.
You are developing an application that uses Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2.
You need to recommend a solution to grant permissions to a specific application for a limited time period.
What should you include in the recommendation?
role assignments
shared access signatures (SAS)
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) identities
account keys
Answer is shared access signatures (SAS)
A shared access signature (SAS) provides secure delegated access to resources in your storage account. With a SAS, you have granular control over how a client can access your data. For example:
What resources the client may access.
What permissions they have to those resources.
How long the SAS is valid.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/common/storage-sas-overview
You use Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 to store data that data scientists and data engineers will query by using Azure Databricks interactive notebooks. Users will have access only to the Data Lake Storage folders that relate to the projects on which they work.
You need to recommend which authentication methods to use for Databricks and Data Lake Storage to provide the users with the appropriate access. The solution must minimize administrative effort and development effort.
Which authentication method should you recommend for each Azure service?
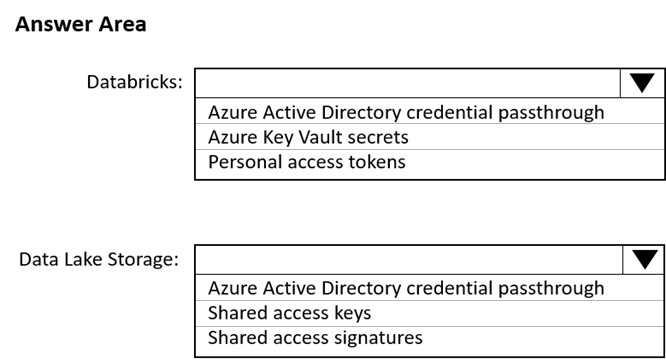
Box 1: Personal access tokens
You can use storage shared access signatures (SAS) to access an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 storage account directly. With SAS, you can restrict access to a storage account using temporary tokens with fine-grained access control.
You can add multiple storage accounts and configure respective SAS token providers in the same Spark session.
Box 2: Azure Active Directory credential passthrough
You can authenticate automatically to Azure Data Lake Storage Gen1 (ADLS Gen1) and Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 (ADLS Gen2) from Azure Databricks clusters using the same Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) identity that you use to log into Azure Databricks. When you enable your cluster for Azure Data Lake
Storage credential passthrough, commands that you run on that cluster can read and write data in Azure Data Lake Storage without requiring you to configure service principal credentials for access to storage.
After configuring Azure Data Lake Storage credential passthrough and creating storage containers, you can access data directly in Azure Data Lake Storage Gen1 using an adl:// path and Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 using an abfss:// path:
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/databricks/data/data-sources/azure/adls-gen2/azure-datalake-gen2-sas-access
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/databricks/security/credential-passthrough/adls-passthrough