DP-203: Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
A company has a Microsoft Azure HDInsight solution that uses different cluster types to process and analyze data. Operations are continuous.
Reports indicate slowdowns during a specific time window.
You need to determine a monitoring solution to track down the issue in the least amount of time.
What should you use?
Azure Log Analytics log search query
Ambari REST API
Azure Monitor Metrics
HDInsight .NET SDK
Azure Log Analytics alert rule query
Answer is Ambari REST API
Ambari is the recommended tool for monitoring the health for any given HDInsight cluster.
Note: Azure HDInsight is a high-availability service that has redundant gateway nodes, head nodes, and ZooKeeper nodes to keep your HDInsight clusters running smoothly. While this ensures that a single failure will not affect the functionality of a cluster, you may still want to monitor cluster health so you are alerted when an issue does arise. Monitoring cluster health refers to monitoring whether all nodes in your cluster and the components that run on them are available and functioning correctly.
Ambari is the recommended tool for monitoring utilization across the whole cluster. The Ambari dashboard shows easily glanceable widgets that display metrics such as CPU, network, YARN memory, and HDFS disk usage. The specific metrics shown depend on cluster type. The “Hosts” tab shows metrics for individual nodes so you can ensure the load on your cluster is evenly distributed.
References:
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/monitoring-on-hdinsight-part-1-an-overview/
You manage a solution that uses Azure HDInsight clusters.
You need to implement a solution to monitor cluster performance and status.
Which technology should you use?
Azure HDInsight .NET SDK
Azure HDInsight REST API
Ambari REST API
Azure Log Analytics
Ambari Web UI
Answer is Ambari Web UI
Ambari is the recommended tool for monitoring utilization across the whole cluster. The Ambari dashboard shows easily glanceable widgets that display metrics such as CPU, network, YARN memory, and HDFS disk usage. The specific metrics shown depend on cluster type. The “Hosts” tab shows metrics for individual nodes so you can ensure the load on your cluster is evenly distributed.
The Apache Ambari project is aimed at making Hadoop management simpler by developing software for provisioning, managing, and monitoring Apache Hadoop clusters. Ambari provides an intuitive, easy-to-use Hadoop management web UI backed by its RESTful APIs.
References:
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/monitoring-on-hdinsight-part-1-an-overview/
You configure monitoring for a Microsoft Azure SQL Data Warehouse implementation. The implementation uses PolyBase to load data from comma-separated value (CSV) files stored in Azure Data Lake Gen 2 using an external table.
Files with an invalid schema cause errors to occur.
You need to monitor for an invalid schema error.
For which error should you monitor?
EXTERNAL TABLE access failed due to internal error: 'Java exception raised on call to HdfsBridge_Connect: Error [com.microsoft.polybase.client.KerberosSecureLogin] occurred while accessing external file.'
EXTERNAL TABLE access failed due to internal error: 'Java exception raised on call to HdfsBridge_Connect: Error [No FileSystem for scheme: wasbs] occurred while accessing external file.'
Cannot execute the query "Remote Query" against OLE DB provider "SQLNCLI11": for linked server "(null)", Query aborted- the maximum reject threshold (o rows) was reached while reading from an external source: 1 rows rejected out of total 1 rows processed.
EXTERNAL TABLE access failed due to internal error: 'Java exception raised on call to HdfsBridge_Connect: Error [Unable to instantiate LoginClass] occurred while accessing external file.'
Answer is "Cannot execute the query "Remote Query" against OLE DB provider "SQLNCLI11": for linked server "(null)", Query aborted- the maximum reject threshold (o rows) was reached while reading from an external source: 1 rows rejected out of total 1 rows processed."
Customer Scenario:
SQL Server 2016 or SQL DW connected to Azure blob storage. The CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE DDL points to a directory (and not a specific file) and the directory contains files with different schemas.
SSMS Error:
Select query on the external table gives the following error:
Msg 7320, Level 16, State 110, Line 14
Cannot execute the query "Remote Query" against OLE DB provider "SQLNCLI11" for linked server "(null)". Query aborted-- the maximum reject threshold (0 rows) was reached while reading from an external source: 1 rows rejected out of total 1 rows processed.
Possible Reason:
The reason this error happens is because each file has different schema. The PolyBase external table DDL when pointed to a directory recursively reads all the files in that directory. When a column or data type mismatch happens, this error could be seen in SSMS.
Possible Solution:
If the data for each table consists of one file, then use the filename in the LOCATION section prepended by the directory of the external files. If there are multiple files per table, put each set of files into different directories in Azure Blob Storage and then you can point LOCATION to the directory instead of a particular file. The latter suggestion is the best practices recommended by SQLCAT even if you have one file per table.
References:
https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/DataCAT/PolyBase-Setup-Errors-and-Possible-Solutions/ba-p/305297
A company uses Azure Data Lake Gen 1 Storage to store big data related to consumer behavior.
You need to implement logging.
Solution: Use information stored in Azure Active Directory reports.
Does the solution meet the goal?
Yes
No
Answer is No
Instead configure Azure Data Lake Storage diagnostics to store logs and metrics in a storage account.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/data-lake-store/data-lake-store-diagnostic-logs
You manage a process that performs analysis of daily web traffic logs on an HDInsight cluster. Each of the 250 web servers generates approximately 10 megabytes (MB) of log data each day. All log data is stored in a single folder in Microsoft Azure Data Lake Storage Gen 2.
You need to improve the performance of the process.
Which two changes should you make?
Combine the daily log files for all servers into one file
Increase the value of the mapreduce.map.memory parameter
Move the log files into folders so that each day’s logs are in their own folder
Increase the number of worker nodes
Increase the value of the hive.tez.container.size parameter
Answer are;
Combine the daily log files for all servers into one file
Move the log files into folders so that each day’s logs are in their own folder
A: Typically, analytics engines such as HDInsight and Azure Data Lake Analytics have a per-file overhead. If you store your data as many small files, this can negatively affect performance. In general, organize your data into larger sized files for better performance (256MB to 100GB in size). Some engines and applications might have trouble efficiently processing files that are greater than 100GB in size.
C: For Hive workloads, partition pruning of time-series data can help some queries read only a subset of the data which improves performance. Those pipelines that ingest time-series data, often place their files with a very structured naming for files and folders. Below is a very common example we see for data that is structured by date:
DataSetYYYYMMDDdatafile_YYYY_MM_DD.tsv
Notice that the datetime information appears both as folders and in the filename.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/blobs/data-lake-storage-performance-tuning-guidance
You have the Diagnostics settings of an Azure Storage account as shown in the following exhibit.
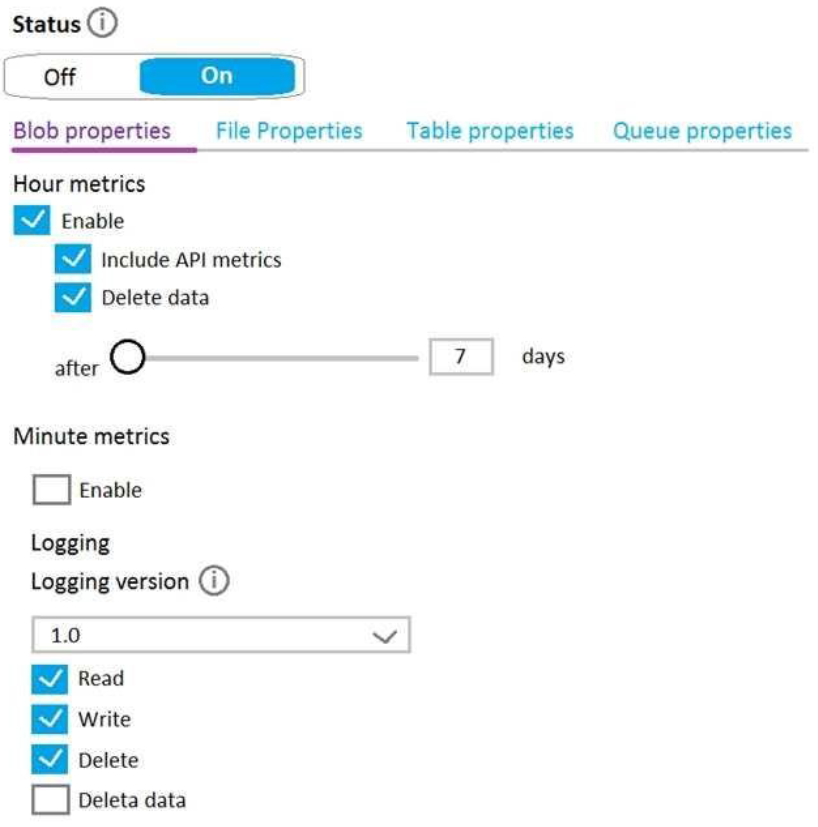
How long will the logging data be retained?
7 days
365 days
indefinitely
90 days
Answer is 7 days
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/common/storage-analytics-metrics
Editor's Note: In my exam, I faced the following question. Please be sure that you have learned what the Watermark delay means.
Your company uses Azure Stream Analytics to monitor devices.
The company plans to double the number of devices that are monitored.
You need to monitor a Stream Analytics job to ensure that there are enough processing resources to handle the additional load.
Which metric should you monitor?
Input Deserialization Errors
Early Input Events
Late Input Events
Watermark delay
Answer is Watermark delay
There are a number of other resource constraints that can cause the streaming pipeline to slow down. The watermark delay metric can rise due to:
- Not enough processing resources in Stream Analytics to handle the volume of input events.
- Not enough throughput within the input event brokers, so they are throttled.
- Output sinks are not provisioned with enough capacity, so they are throttled. The possible solutions vary widely based on the flavor of output service being used.
Deserialization issues are caused when the input stream of your Stream Analytics job contains malformed messages.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/stream-analytics/stream-analytics-time-handling
You have an Azure Stream Analytics job.
You need to ensure that the job has enough streaming units provisioned.
You configure monitoring of the SU% Utilization metric.
Which two additional metrics should you monitor?
Watermark Delay
Late Input Events
Out of order Events
Backlogged Input Events
Function Events
Late Input Events: events that arrived later than the configured late arrival tolerance window.
Note: While comparing utilization over a period of time, use event rate metrics. InputEvents and OutputEvents metrics show how many events were read and processed.
Backlogged Input Events: In job diagram, there is a per partition backlog event metric for each input. If the backlog event metric keeps increasing, it’s also an indicator that the system resource is constrained (either because of output sink throttling, or high CPU).
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/stream-analytics/stream-analytics-scale-jobs
Which two metrics should you use to identify the appropriate RU/s for the telemetry data? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
Number of requests
Number of requests exceeded capacity
End to end observed read latency at the 99th percentile
Session consistency
Data + Index storage consumed
Avg Throughput/s
Answer is Number of requests Data + Index storage consumed
Scenario: The telemetry data must be monitored for performance issues. You must adjust the Cosmos DB Request Units per second (RU/s) to maintain a performance SLA while minimizing the cost of the RU/s. With Azure Cosmos DB, you pay for the throughput you provision and the storage you consume on an hourly basis. While you estimate the number of RUs per second to provision, consider the following factors: Item size: As the size of an item increases, the number of RUs consumed to read or write the item also increases.
You develop data engineering solutions for a company.
A project requires the deployment of resources to Microsoft Azure for batch data processing on Azure HDInsight. Batch processing will run daily and must:
- Scale to minimize costs
- Be monitored for cluster performance
Solution: Monitor clusters by using Azure Log Analytics and HDInsight cluster management solutions.
Does the solution meet the goal?
Yes
No
Answer is Yes
HDInsight provides cluster-specific management solutions that you can add for Azure Monitor logs. Management solutions add functionality to Azure Monitor logs, providing additional data and analysis tools. These solutions collect important performance metrics from your HDInsight clusters and provide the tools to search the metrics. These solutions also provide visualizations and dashboards for most cluster types supported in HDInsight. By using the metrics that you collect with the solution, you can create custom monitoring rules and alerts.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/hdinsight/hdinsight-hadoop-oms-log-analytics-tutorial