AZ-104: Microsoft Azure Administrator
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscription1 contains two Azure virtual machines VM1 and VM2. VM1 and VM2 run Windows Server 2016.
VM1 is backed up daily by Azure Backup without using the Azure Backup agent.
VM1 is affected by ransomware that encrypts data.
You need to restore the latest backup of VM1.
To which location can you restore the backup?
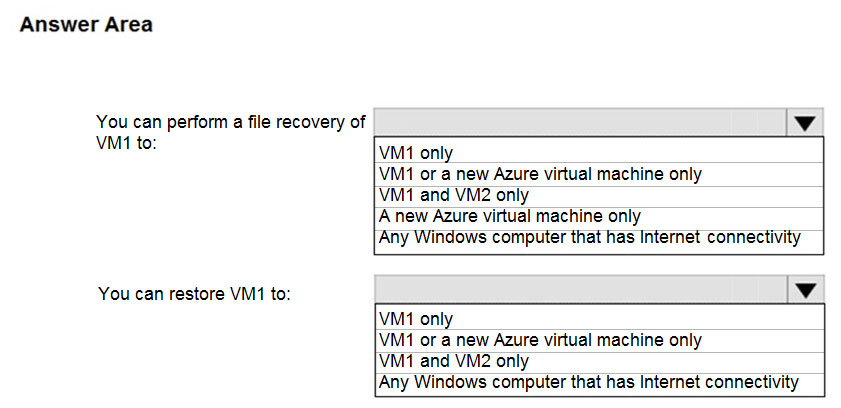
Box 1: Any Windows computer that has Internet connectivity
For files recovery, you download and run a windows executable to map a network drive. It can only run when the OS meets the requirements. Any computer running Windows Server 2016 or Windows 10 is suitable. File recovery can be done from any machine on the Internet.
Note: There might be compatibility issues with any Windows computer, so consider VM1 and VM2 only as an answer.
Box 2: VM1 or a new Azure virtual machine only
For restoring a VM, you can choose 'Create new' or 'Replace existing'.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/backup/backup-azure-restore-files-from-vm
https://github.com/MicrosoftDocs/azure-docs/blob/master/articles/backup/backup-azure-restore-files-from-vm.md#for-windows-os
You create an Azure VM named VM1 that runs Windows Server 2019.
VM1 is configured as shown in the exhibit.
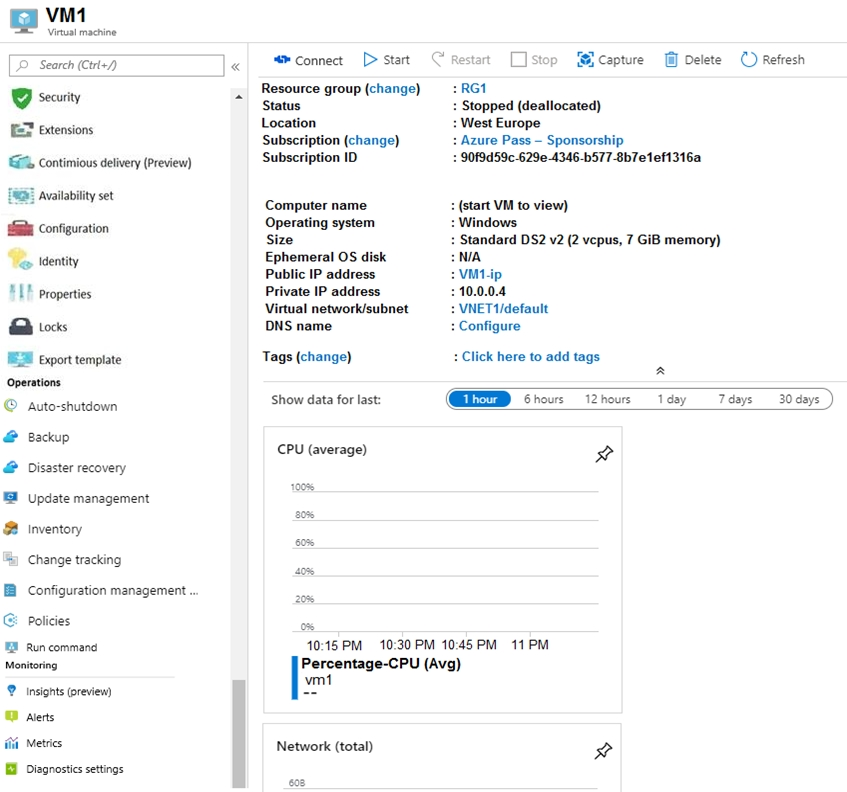
You need to enable Desired State Configuration for VM1.
What should you do first?
Connect to VM1.
Start VM1.
Capture a snapshot of VM1.
Configure a DNS name for VM1.
Answer is Start VM1.
Status is Stopped (Deallocated). The DSC extension for Windows requires that the target Virtual Machine is able to communicate with Azure. First you start the VM, because you need VM online to deploy DSC Extension.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/extensions/dsc-windows
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscription1 contains a virtual machine named VM1.
You have a computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 10. Computer1 is connected to the Internet.
You add a network interface named vm1173 to VM1 as shown in the exhibit.
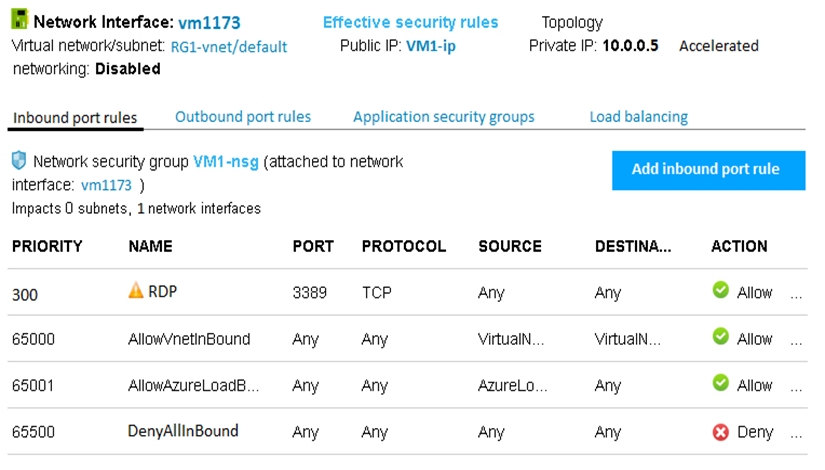
From Computer1, you attempt to connect to VM1 by using Remote Desktop, but the connection fails.
You need to establish a Remote Desktop connection to VM1.
What should you do first?
Change the priority of the RDP rule
Attach a network interface
Delete the DenyAllInBound rule
Start VM1
Answer is Start VM1
Αny resource with a dynamically assigned public IP address will display the 'name' you gave it when the resource it is assigned to is offline. A static address will be shown regardless of the resource state. This means that we need to start the VM1.
A: RDP rule has the highest priority. priority.
B: The network interface has already been added to VM1.
C: DenyAllInBound has really low priority.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/security-overview
Your company has serval departments. Each department has a number of virtual machines (VMs).
The company has an Azure subscription that contains a resource group named RG1.
All VMs are located in RG1.
You want to associate each VM with its respective department.
What should you do?
Create Azure Management Groups for each department.
Create a resource group for each department.
Assign tags to the virtual machines.
Modify the settings of the virtual machines.
Answer is Assign tags to the virtual machines.
The correct approach to associate each VM with its respective department without restructuring the resource groups is to use Azure Tags. Azure Tags allow you to associate metadata with resources to categorize and organize them based on your organization's needs.
A. Create Azure Management Groups for each department. This would not be the correct approach for the given scenario. Azure Management Groups are designed to manage access, policies, and compliance across multiple Azure subscriptions.
B. Create a resource group for each department. This approach would involve restructuring the resources, and you'd have to move VMs between resource groups. It's a more disruptive approach than simply tagging the VMs.
C. Assign tags to the virtual machines. This is the correct approach. Tags allow you to categorize resources without changing their actual configuration or moving them between resource groups.
D. Modify the settings of the virtual machines. This is too vague and doesn't specify which settings would be changed. Simply modifying VM settings wouldn't inherently associate a VM with a department.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-resource-manager/resource-group-using-tags
You have the App Service plans shown in the following table.

You plan to create the Azure web apps shown in the following table.

You need to identify which App Service plans can be used for the web apps.
What should you identify?
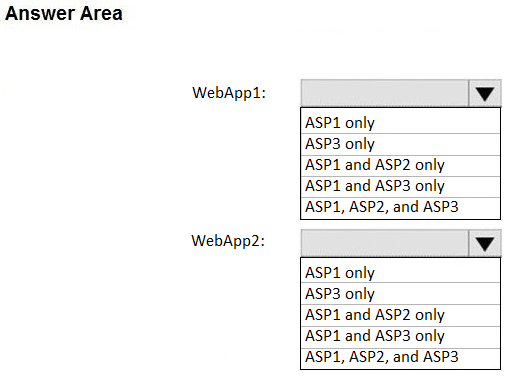
Box 1: ASP1 and ASP3 only
ASP.NET Core apps can be hosted both on Windows or Linux.
The region in which your app runs is the region of the App Service Plan is in.
ASP2 is in Central US, not the same as WebApp1. Different locations.
Box 2: ASP1 only
ASP.NET apps can be hosted on Windows only. Only ASP1 is in the same Location as the WebApp2 (West US).
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/quickstart-dotnetcore?pivots=platform-linux
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/app-service-plan-manage
You have an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster named AKS1 and a computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 10. Computer1 that has the Azure CLI installed.
You need to install the kubectl client on Computer1.
Which command should you run?
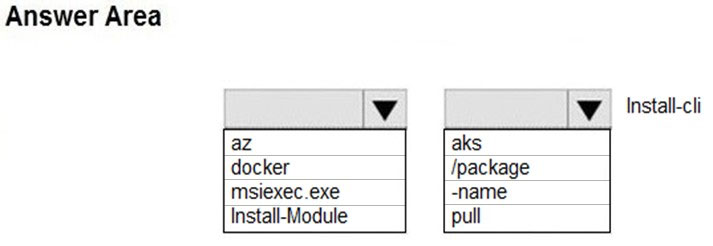
Answers are az and aks
To install kubectl locally, use the az aks install-cli command.
Note: Azure cli commands start with az. We use Install-Module to install a Powershell module.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/aks/kubernetes-walkthrough
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/reference-index?view=azure-cli-latest
You create an App Service plan named Plan1 and an Azure web app named webapp1.
You discover that the option to create a staging slot is unavailable.
You need to create a staging slot for Plan1.
What should you do first?
From Plan1, scale up the App Service plan
From webapp1, modify the Application settings
From webapp1, add a custom domain
From Plan1, scale out the App Service plan
Answer is From Plan1, scale up the App Service plan
The app must be running in the Standard, Premium, or Isolated tier in order for you to enable multiple deployment slots.
If the app isn't already in the Standard, Premium, or Isolated tier, you receive a message that indicates the supported tiers for enabling staged publishing. At this point, you have the option to select Upgrade and go to the Scale tab of your app before continuing.
Scale up: Get more CPU, memory, disk space, and extra features like dedicated virtual machines (VMs), custom domains and certificates, staging slots, autoscaling, and more.
Incorrect:
Scale out: Increase the number of VM instances that run your app. You can scale out to as many as 30 instances
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/deploy-staging-slots
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/manage-scale-up
You have a deployment template named Template1 that is used to deploy 10 Azure web apps.
You need to identify what to deploy before you deploy Template1. The solution must minimize Azure costs.
What should you identify?
five Azure Application Gateways
one App Service plan
10 App Service plans
one Azure Traffic Manager
one Azure Application Gateway
Answer is one App Service plan
Creating one App Service Plan, you can support up to 10 Web Apps. Adding any of the other resources are pointless and not noted as a requirement.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/overview-hosting-plans
You plan to create the Azure web apps shown in the following table.
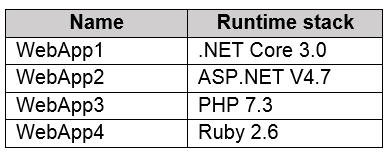
What is the minimum number of App Service plans you should create for the web apps?
1
2
3
4
Answer is 2
.NET Core 3.0: Windows and Linux
ASP .NET V4.7: Windows only
PHP 7.3: Windows and Linux
Ruby 2.6: Linux only
Also, you can’t use Windows and Linux Apps in the same App Service Plan, beacuse when you create a new App Service plan you have to choose the OS type. You can't mix Windows and Linux apps in the same App Service plan.
So, you need 2 ASPs.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/overview
You create the following resources in an Azure subscription:
- An Azure Container Registry instance named Registry1
- An Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster named Cluster1
You create a container image named App1 on your administrative workstation.
You need to deploy App1 to Cluster1.
What should you do first?
Run the docker push command.
Create an App Service plan.
Run the az acr build command.
Run the az aks create command.
Answer is Run the az acr build command.
az acr build will build and push the image at the same time. Queues a quick build, providing streaming logs for an Azure Container Registry.
docker build/push will do the same thing, but you will have to configure docker to login to the container registry.
If we go with Answer A, then we need the following:
- Make sure that ACR is integrated to AKS.
- docker tag has been run with the right ACR.
- docker push
- create kubectl apply with the right deployment and right ACR.
In case we go with Answer C.
- No need for docker push or tag.
- still need to make sure that ACR is integrated to AKS.
- then run kubectl apply
Note: If answer C is missing from the exam, then select A.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/aks-deploy-container-app/5-exercise-deploy-app